Our Location
Metal laser cutting originated in the 1960s and requires high power. Today, laser cutters can accurately and quickly cut aluminum, steel, titanium, copper, and brass. It’s a primary method for low—to mid-volume components, heavy machinery parts, and aerospace manufacturing. This article covers sheet metal laser cutting, its history, advantages, disadvantages, and laser types.

Table of Contents
ToggleLaser cutting is a precise CNC (Computer Numerical Control) technique for fabricating sheet metal. It involves using high-power laser beams that are focused and adjusted to cut sheet metal into specific sizes and shapes. An assist gas is combined with the laser beam to burn the metal into the desired shape or size. Although sheet metal for laser cutting may seem complex, it offers unparalleled speed, precision, and versatility that cannot be found in other steel sheet cutting techniques.
The history of metal laser cutting dates back to the early 1960s when the first lasers were invented. In 1965, Kumar Patel from Bell Labs developed a machine that could cut metals. However, the early machines required much power to operate. With the development of CO2 lasers in the 1970s, the efficiency and practicality of the machines improved. By the 1980s, the technology had advanced, moving out of research and military manufacturing into the mainstream.
In the early 2000s, the development of fiber lasers increased power efficiency and led to machines that produced higher-quality cuts. Computer-aided design and computer-aided manufacturing software have increased the accessibility of laser cutting. Moreover, small and low-cost home-use machines that are increasingly widespread and capable have further democratized the technology.

C. Kumar N. Patel
The sheet metal laser cutting process begins with a computer program that directs a high-intensity laser beam onto the metal to be cut. The laser beam is directed onto the workpiece with the help of mirrors placed in various positions. A high-quality lens then focuses the intense beam onto a small spot on the surface of the workpiece. Before cutting, the tiny spot is first pierced.
The laser beam in this process comprises photons and is about 1/5 of a millimeter wide. The beam can also concentrate 1000 to 2000 watts of energy, a considerable amount of energy in a single beam.
When the intense beam of light hits the material, it heats up, causing the area to melt, burn, or vaporize, even if the heat isn’t enough. As a result, it leaves a very accurate outline per the initial CAD design.
You have several options when investing in a laser machine for sheet metal cutting.
A moving material laser cutter projects a stationary light beam and uses a mobile surface that moves automatically in pre-programmed directions to connect workpieces. The directions are programmed using computers. While this equipment is accurate and precise in laser cut steel sheet, it tends to be slower than other laser cutters.
Flying optic laser cutters are fast and affordable cutting equipment. They use a powerful beam of light to cut along a metal sheet’s X and Y axes, allowing you to cut many workpieces quickly. These machines are multidimensional and fast, making them ideal for industrial use.
Pulsed laser cutting machines produce high power output for a short period, making them perfect for piercing. The machines quickly project high power, making them ideal for industrial use.
Punch laser cutters are high-power machines that can cut metal with up to 3500 watts. They can perform various tasks, such as punching, marking, contouring, and bending. Their primary purpose is to cut intricate inner contours and outer parts.
Crystal or diode-pumped solid-state lasers emit laser light in specific frequency bands using semiconductors with dopants. They are vital for fiber lasers and low-power laser cutting machines. Nonetheless, their power is limited, with the highest power devices only a few hundred watts.
This type of laser is suitable for cutting, boring, and engraving on metal surfaces. It uses radio frequency energy to cut mild steel, aluminum, stainless steel, and titanium. CO2 lasers are most commonly used in industrial applications.
A fiber laser is a solid-state laser that uses a solid gain medium instead of gas or liquid. In this system, seed laser beams are amplified inside glass fibers. It is important to note that fiber lasers are not commonly used in metal fabrication.

Laser steel cutting efficiently cuts the metal into various shapes and sizes. This method can cut materials with unique features for different applications. Here are some such materials.
Aluminum is a lightweight material used in applications that require corrosion resistance, such as the automobile, aerospace, and consumer electronics industries.
Steel is available in different forms, each with its features. Mild steel is affordable and versatile, making it a popular choice. Stainless steel is known for its long-lasting finish and resistance to corrosion. Cutting stainless steel sheets is used in applications that require a high level of strength.
Copper is used in electronic applications and offers conductivity and corrosion resistance. Electronic components are manufactured using sheet metal cutting.
Brass is a zinc and copper mixture with an aesthetically appealing look. Hence, it is used with sheet metal laser cutting for aesthetic uplift applications.
Nickel is a durable material that resists high temperatures and corrosion. Hence, it is used in applications like chemical processing and aerospace.
Titanium is used in the automobile, aerospace, and medical sectors. It is strong, lightweight, and well-suited for the sheet metal cutting process.
Galvanized steel is used when laser cutting sheet metal and is ideal for applications that require a corrosion-resistant material consisting of a zinc layer.
The choice of sheet metal laser cutting material depends on the application’s requirements, such as strength, budget, and other factors. The material’s properties must be assessed before selection to ensure suitability.
After laser cutting sheet metal, some components may need post-processing. Suggested methods include:
Laser etching is a process that can create permanent marks on the components. This method is expensive and involves using high temperatures to melt the metal to create identification marks. Many brands use this method to create their brand labels or points of identification.
Painting involves adding a coat of paint to the metal surface. Layers of paint are sprayed onto the metal, improving the finishing and layout of the surface. This process can also help to remove defects or conceal faults on the surface of the metal. However, painting is less durable than other finishing methods.
Passivation is a protection process used to prevent corrosion and create an oxide layer that adds an extra layer of protection to the component. This process involves treating the material with a citric and nitric acid bath. However, before passivation can occur, the sheet metal’s surface needs to be cleaned.
Electroplating is a process that uses electricity and an electrolytic cell to apply a metal layer to a component. This process creates a bond that improves the metal’s functionality and aesthetics, reducing friction between moving parts and protecting against corrosion. It also enhances the metal’s adhesion properties.
Chemical films are an affordable finishing material that involves applying a chemical coating layer. This method is suitable for aluminum and acts as a primer for the metal surface, helping to reduce the chance of corrosion.
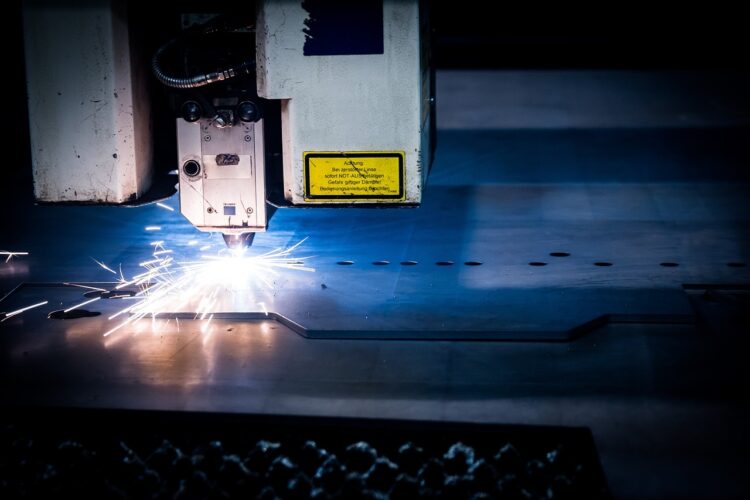
Sheet metal laser cutting has several advantages:
Other benefits of sheet metal laser cutting include:
– Narrow kerf widths
– High overall finish quality
– High-speed cutting
– Elimination of the need for any secondary finishing operations
– Minimal operator intervention is required.
– Minimal material wastage
Sheet metal laser cutting has several disadvantages, which are listed below:
– The equipment is expensive, and it needs to work hard to justify its cost. Ancillary and maintenance costs can also be high.
– The cuts are not square but rely on a collimated energy beam, resulting in an angled cut. This effect is minimal on thin materials but can be significant on thicker targets.
– Inert gas assistance is required to blow the cut clean to cut some metals effectively. This process increases gas consumption, which is a cost factor.
– Safety issues regarding laser cutting can be a burden.
– Health issues are also a concern because laser cutting metal can produce nano-particle dust poses a hazard to the operator. Non-metals can produce toxic vapors and smoke, so no cut should be considered completely safe for the user.
– Oxygen assist is also necessary to clean the cut and accelerate the cutting by “burning.”
When cutting sheet metal with laser cutting, it’s essential to minimize waste to ensure cost efficiency. By controlling sheet metal material waste, your company can save money and minimize landfill waste while reducing emissions caused by unnecessary laser-cutting machines. Here are some ways to minimize material waste during laser cutting:
1. Make your design drawing more efficient by introducing shared cut lines. Place rectangular edges so that they share straight lines on the part rather than creating unnecessary spaces between shapes. This method eliminates waste and shortens the laser cutter’s cutting path, reducing run time and cost.
2. Keep workpieces close together during cutting. Nesting parts together minimizes material waste since it’s a CNC process.
3. Avoid intricate designs. Unnecessarily complex shapes and curves slow down laser cutting, wasting material.
4. Offcuts are unavoidable in many sheet metal fabrication processes. However, maximizing offcuts and avoiding waste in laser cutting is possible. You can, for instance, reuse them to cut out smaller, more delicate parts or for test runs. Store your offcuts properly so they’re ready for your next laser-cutting project.
This technology offers exact measurements, making it ideal for manufacturing precision metal parts in automotive, aerospace, and military applications. Laser cutters provide dimensional tolerances as tight as ± 0.0005 inches, the smallest kerf width possible. They are also the fastest tools for cutting thin materials of 16 gauge or less. Mild steel up to 1.25 inches thick can be cut with a more powerful laser-cutting machine. However, it’s crucial to consider that tighter tolerances increase the cost of laser custom cut sheet metal parts. So, unless your part requires tight tolerances for form, fit, or function, it’s best to avoid them.
When it comes to laser cutting, the quality of your equipment determines the quality of your cuts. Regular maintenance can help reduce irregularities, but it’s also essential to consider the cutting parameters for the best results. These parameters include:
– Surface roughness: A smooth and rust-free material surface produces better cutting quality.
– Sheet Metal thickness: The metal’s nature and thickness must match the laser cutter’s wattage for better results.
– Cutting focus: Accurate focusing is critical for the best cutting results.
– Cutting speed: The speed should neither be fast nor slow. It depends on the material’s thickness and composition.
Controlling these parameters is necessary when performing multiple identical cuts to avoid making the same mistakes. To design appropriately for laser cutting, use the right software and keep the drawing simple with full-scale dimensions. Choose the appropriate metal material for your intended application, such as aluminum for signs and steel for commercial and industrial purposes.
Important tips for sheet metal laser cutting:
– Ensure sufficient power for the maximum thickness.
– Use a CO2 or CNC fiber laser machine.
– Keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
– Keep workspace and machine clean.
– Use appropriate machine settings for the material.
– Test cuts in a waste area for quality.
– Ensure proper design for clean single-pass cut.
– Use enough assistance for a quality cut and clear optics.
– Wear safety gear and use good ventilation.

If you want to start a sheet metal laser cutting project for your business, choosing a company that provides high-quality laser cut sheet metal service is essential. The right sheet metal cutting service can significantly impact the quality of your final products. Here are some features that you should look for when selecting the right supplier:
1. Suppliers should have a good track record of experience, provide excellent metal sheet cutting service, offer proper design solutions, and utilize top-of-the-line equipment.
2. The sheet metal laser cutting supplier should provide you with special CAD software for free to design a part from scratch or adapt an existing design to your needs.
3. Choose a company that can handle the material you need to get laser-cut.
5. The company should provide excellent technical support to solve problems quickly.
4. The company should have high-quality machinery to produce parts that perfectly match your designs. The cutting equipment should be durable and reliable to reduce the risk of interruptions during production.
6. Ordering the product should be easy and save time and effort.
7. While cost is crucial, don’t hire a company based on cost alone, as it could affect quality and availability.
9. Choose a laser cutting service with knowledgeable sales engineers who can execute your work quickly and cost-effectively to the highest standard.
8. The service provider you choose must be accredited for their services and the quality of their products. The standard accreditation is ISO 9001:2015 and BS/EN 1090-1.
Sheet metal laser cutting is a complex task, and you will only be satisfied with the result if you carefully choose the supplier you work with. The company should be able to understand your vision and design an appropriate product without causing you any trouble. They should then be able to execute the designs while paying attention to the minor details so you’re delighted with the finished laser-cutting product.
What material is not suitable to cut using a laser cutter?
Polycarbonate and ABS Melts/Cyanide ABS are unsuitable for laser cutting due to the production of soot and poor cut quality.
Is Laser Cutting Sheet Metal Process Dangerous?
Laser cutting in sheet metals is safe if safety precautions are followed. However, laser cutting has extra risks, such as the “hot” aspect and coherent light. Small laser cutters are safe, but be careful of backscatter. Don’t run the machine with the covers open. Keep an extinguisher close. Clean the extraction system and machine after use to avoid health hazards from dust. Overall, the user hazards are minor and manageable.
Can a laser cut galvanized steel?
Laser cutting galvanized steel is highly compatible with laser cutting. However, the galvanization does not permeate the metal, thus exposing the edges to potential corrosion. Once assembled, additional protection may be necessary for the cut edges.
Sheet metal laser cutting produces accurate and complex parts. It is one of the best technologies for the sheet metal fabrication process. Contact us now if you need sheet metal laser cutting. We have a trained team ready to handle all your laser-cutting needs.

